| Media Supplements (Ndiff N2) | ||||||
| 品牌 | Code No. | 产品名称 | 包装量 | 价格(元) | 说明书 | 数量 |
| Cellartis | Y40100 | NDiff® N2 | 5 ml | ¥2,087 | |
  |
收藏产品 加入购物车
| NDiff 细胞培养添加物 | ||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
 |
||||||||||||||||||
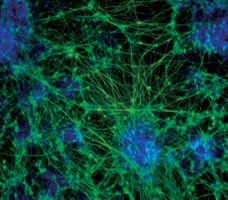
| Mouse embryonic stem cells differentiate into neurons when cultured in adherent monoculture with NDiff N2-supplemented basal media. The differentiated cells express neuron-specific class III beta-tubulin (TuJ1, green). | ||||||||||||||||||
| 参考文献: | ||||||||||||||||||
| 1. Bottenstein JE, Cell Culture in the Neurosciences. Plenum Press (1985) New York and London. 2. Ying QL, et al. (2003) Conversion of embryonic stem cells into neuroectodermal precursors in adherent monoculture. Nature Biotechnology 21:183-186. 3. Ying QL, Smith AG. (2003) Defined conditions for neural commitment and differentiation. Methods Enzymol. 365:327-341. 4. Conti L, et al. (2005) Niche-independent symmetrical self-renewal of a mammalian tissue stem cell. PLoS Biol. 3(9):e283. 5. Pollard SM, et al. (2006) Adherent neural stem (NS) cells from fetal and adult forebrain. Cereb. Cortex 16 Suppl 1:112-20. 6. Conti L, et al. (2006) Neural stem cell systems: diversities and properties after transplantation in animal models of diseases. Brain Pathol. (2006) 16(2):143-154. 7. Nichols J, Ying QL. (2006) Derivation and propagation of embryonic stem cells in serum- and feeder-free culture. Methods Mol Biol. 329:91-98. 8. Hook L, et al. (2011) Non-immortalized human neural stem (NS) cells as a scalable platform for cellular assays. Neurochem Int. 59(3): 432-44. |
||||||||||||||||||
